TLDR¶
• Core Points: Opera One R3 enhances tab management with expanded Tab Islands, introduces a faster, more context-aware built-in AI, and broadens the sidebar to include Google services and more flexible split-screen layouts.
• Main Content: The release broadens customization, improves AI responsiveness, and enriches the user experience with expanded sidebar options and layout versatility.
• Key Insights: Opera continues layering productivity-focused features, aiming to reduce context switching and boost efficiency across browsing, work, and AI-assisted tasks.
• Considerations: Users should evaluate how Tab Islands and AI capabilities align with their workflow, and consider any potential impacts on browser performance and privacy.
• Recommended Actions: Update to Opera One R3 to experiment with new tab management, AI, and sidebar features; tailor Tab Islands and AI prompts to fit daily routines.
Content Overview¶
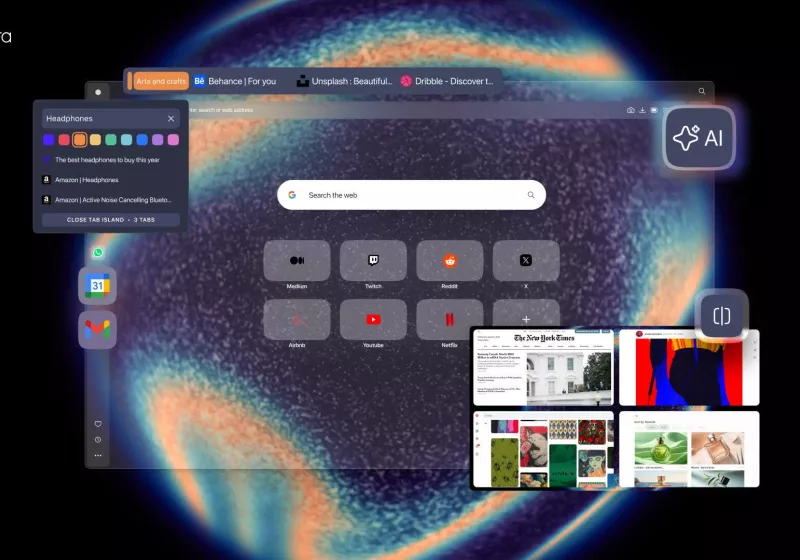
Opera One R3 marks a substantial milestone in Opera’s ongoing effort to blend advanced tab management, AI-driven assistance, and a more capable interface into a single browser experience. The update centers on three core enhancements: expanded Tab Islands for tab organization, a faster, context-aware built-in AI, and a more versatile sidebar that connects with Google services while introducing expanded split-screen layouts. Taken together, these changes aim to streamline daily browsing, boost productivity, and reduce friction when juggling multiple tasks, whether the user is researching, coding, writing, or multitasking across applications.
Tab Islands first appeared as a way to group related tabs, helping users switch contexts without losing track of their work. R3 extends this feature, giving users more customization options to define islands, label groups, and manage tab clusters more intuitively. The focus is on reducing tab clutter and enabling quick transitions between different projects or topics. In practice, users can create, rename, and reorganize islands with greater flexibility, and apply visual cues or rules to automate organization. This expansion is particularly meaningful for power users who routinely work with dozens of tabs across multiple subjects or projects.
The built-in AI receives a notable upgrade in speed and contextual understanding. Opera emphasizes that the AI responds faster and with better awareness of the user’s current task, historical browsing patterns, and the content of open tabs. This translates into smarter suggestions, faster summaries of articles or research, and more precise assistance when drafting emails, notes, or code. While the AI remains optional, it’s designed to complement browsing rather than overwhelm it, surfacing contextual help when it’s most useful and interrupting less frequently.
A key element of the R3 update is an expanded, more capable sidebar. The sidebar now offers deeper integration with Google services, broadening access to tools and workflows within the browser itself. This expansion supports a more seamless cross-application experience, enabling users to perform tasks such as email checks, calendar lookups, document access, and other services without leaving the browser environment. The sidebar has also been enhanced to support more flexible split-screen layouts, making it easier to view and work with multiple windows side-by-side. This is particularly advantageous for users who need to reference data while drafting content, compare sources, or monitor multiple streams of information simultaneously.
Opera’s emphasis on customization, speed, and AI-assisted productivity reflects a broader trend in modern browsers: the shift from simply rendering pages to acting as a centralized workspace. R3’s combination of tab islands, faster AI, and an expanded Google-enabled sidebar signals an intent to reduce the cognitive load that comes with multitasking across tabs, apps, and documents. As with any major feature upgrade, the real-world impact will depend on how users adopt and adapt these capabilities to fit their workflows and privacy comfort levels.
In-Depth Analysis¶
Opera One R3 represents a deliberate refinement of the browser’s core productivity toolkit. The expanded Tab Islands feature is more than a cosmetic upgrade; it is an operating model adjustment for tab management. By increasing customization options, Opera provides users with a more granular method to partition their browsing activities. The ability to create, rename, and visually organize islands—potentially with consistent color schemes, icons, or labeling strategies—can help maintain a mental map of ongoing tasks. For knowledge workers juggling research, email, and collaborative workspaces, this can translate into increased focus and faster navigation between relevant clusters of tabs.
From a performance perspective, the AI upgrade aims to deliver faster, more context-aware assistance. The emphasis on speed and contextual relevance means users are more likely to rely on AI-assisted features for summarization, extraction of key points, rewriting suggestions, and quick drafting tasks. The underlying improvements may include optimizations in the AI inference pipeline, better on-device caching, and smarter prompt handling that leverages the content of currently open tabs and user routines. While the AI remains optional, its enhanced responsiveness could change how often users engage with it, potentially reducing the time spent on repetitive tasks and enabling quicker decisions.
The expanded sidebar with Google services broadens the browser’s integrated workflow capabilities. By embedding access to Gmail, Google Calendar, Drive, and other Google tools within the sidebar, Opera attempts to create a more cohesive ecosystem. This reduces the need to switch between tabs and external apps, keeping essential tools reachable within a single interface. The added flexibility for split-screen layouts further enhances multi-tasking potential by allowing users to arrange windows and side-by-side views more freely. For example, a user might keep a research document visible in one pane while cross-referencing citations or streaming relevant data in another.
From a usability angle, these features are most beneficial when they align with established workflows. Users who frequently operate multiple projects in parallel—such as students, researchers, developers, and content creators—could experience tangible gains in efficiency. The ability to structure tab islands around specific topics or projects, coupled with the AI’s ability to produce summaries and actionable insights, creates a streamlined path from information gathering to output. The Google-enabled sidebar and expanded split-screen layouts add layers of convenience, enabling quick access to commonly used tools without heavy context switching.
However, the integration of more tools and the richer feature set also introduce potential trade-offs. Increased customization options and AI features can raise concerns about privacy, data handling, and resource usage. While Opera has a track record of offering robust controls, users should review permissions, data sharing policies, and options to limit AI data collection or disable features entirely. Device performance can also be a consideration; even well-optimized features may have a marginal impact on battery life and memory usage when used aggressively, particularly on lower-powered devices. Opera’s documentation and settings should ideally provide clear guidance on how to balance productivity with privacy and performance preferences.
In terms of user experience, the update appears to be designed with a modular philosophy: give users granular control over how they organize tabs, how they interact with AI, and how they access tools through the sidebar. This modular approach can reduce cognitive load by letting users opt into features they value most and ignore those that do not align with their workflow. The result could be a more personalized and efficient browsing experience, where routine tasks become more automatic and less disruptive.
The R3 release’s broader strategic implication is that Opera continues to position itself as a productivity-oriented alternative to traditional browsers. By weaving together improved tab organization, proactive AI support, and integrated tool access, Opera seeks to create a more self-contained browsing environment. If successful, this could influence user expectations for browser design, pushing competitors to enhance their own tab management capabilities, AI features, and sidebar integrations.
Nevertheless, there are questions about long-term adoption and interoperability. How well Tab Islands scale with extremely large tab collections remains to be seen, as does the AI’s ability to maintain high-quality, contextually appropriate outputs over extended sessions. Compatibility with various web apps, extensions, and enterprise environments will also shape adoption in professional contexts. Opera’s ongoing development will likely need to address edge cases such as how islands behave when tab counts surge, how AI handles sensitive information, and how the sidebar interacts with corporate identity providers or privacy policies.
From a design perspective, R3’s usability hinges on discoverability and non-intrusiveness. As feature sets expand, there is a risk that new users may feel overwhelmed by options. Effective onboarding, contextual help, and clear control over feature visibility become essential to ensuring that the enhancements enhance rather than complicate the browsing experience. Opera can further improve this by offering guided setups for common workflows, presets for different user personas (researchers, developers, students, writers), and straightforward privacy toggles for AI features.
In terms of future directions, R3 could evolve along several axes. One potential path is deeper AI customization, enabling users to tailor AI behavior to specific tasks or domains, such as summarization for legal research, code assistance for developers, or writing prompts for content creators. Another avenue is more granular tab island management, such as auto-sorting by domain, priority tagging, or integration with task management tools. Expanded interoperability with other ecosystems beyond Google services might also be explored, broadening the utility of the sidebar for users invested in different productivity suites. Finally, performance optimizations and transparent privacy controls will be critical as feature sets become more sophisticated and data-intensive.
Overall, Opera One R3 represents a thoughtful consolidation of productivity-oriented features that align with contemporary research, writing, and multitasking workflows. By improving tab organization, AI assistance, and sidebar capabilities, Opera aims to reduce friction in daily browsing and create a more efficient pathway from information discovery to action. The real measure of success will be how seamlessly users can integrate these elements into their habits and how well the browser’s performance and privacy settings support those habits over time.
*圖片來源:Unsplash*
Perspectives and Impact¶
The Opera One R3 update arrives at a moment when users increasingly expect browsers to function as a central workbench rather than a simple gateway to web pages. The updated Tab Islands reflect a shift toward task-centric organization, enabling users to group related tabs into dedicated workspaces. For teams and individuals managing multiple streams of research, writing projects, or development tasks, this can significantly alter navigation patterns. The ability to customize islands, rename them, and apply visual cues makes it easier to maintain a mental model of ongoing work, potentially reducing cognitive load and boosting focus.
AI integration in R3 emphasizes fast, contextual support. As AI becomes more embedded in daily browsing, users may rely on the assistant to summarize articles, extract key points, draft notes, or provide code snippets inline. The success of this approach depends on maintaining a balance between helpful automation and user autonomy. If the AI is too aggressive, it can interrupt or misinterpret a user’s intent; if too passive, it may fail to deliver timely value. Opera’s approach to transparency, controls, and user feedback will influence whether the AI feature becomes a dependable partner rather than a nuisance.
The expanded Google services in the sidebar reflect a broader trend of integrating widely used productivity tools directly into the browser interface. This can lead to shorter task cycles, as users can access email, calendars, documents, and other resources without switching contexts. The extended split-screen capabilities further support multi-source comparison, research workflows, and simultaneous content creation. However, this tight integration also raises questions about data governance, especially in enterprise or shared device scenarios. Clear privacy options and enterprise-friendly settings will be important for broader adoption in professional contexts.
From an industry standpoint, Opera’s R3 update may push competitors to enhance their own tab management and AI features. If R3 proves effective in improving productivity without sacrificing performance, it could set new expectations for how browsers balance power-user features with everyday usability. This could lead to a wave of feature experiments across major browsers, with more emphasis on context-aware AI, workspace-like tab organization, and integrated productivity dashboards.
Long-term implications for users include evolving workflows and new habits. As people grow accustomed to tab islands, AI prompts, and a feature-rich sidebar, their interaction patterns with the browser may become more task-focused. This could influence how users allocate screen real estate, how they structure their day around AI-assisted insights, and how they manage privacy settings to protect sensitive information. The extent to which users adopt these changes will depend on the perceived value delivered and the degree of control provided over features and data.
In terms of accessibility, Opera’s enhancements also offer potential benefits. A more organized tab structure can aid users who rely on keyboard navigation and screen readers, provided the UI design embraces accessible patterns and responsive feedback. AI-powered summaries and inline suggestions can help users with information processing, though accessibility considerations must be addressed to ensure the AI outputs are clear, non-confusing, and easily navigable within assistive technologies.
Future research and development directions could explore smarter, user-driven automation rules for Tab Islands, such as dynamic reorganization based on time of day or activity type. Enhanced AI explainability features—where the assistant clarifies why it suggests a particular action or summary—could improve trust and adoption. The ongoing interplay between privacy controls, data minimization, and on-device processing will remain a focal point as AI capabilities expand within browsers.
In sum, Opera One R3 augments a browser that already emphasizes productivity and efficiency. By refining how users organize tabs, accelerating AI-driven assistance, and enriching the sidebar with Google services and flexible layouts, Opera seeks to transform the browser into a more capable, cohesive work environment. The update’s success will hinge on practical usability, performance stability, and transparent privacy governance across diverse user contexts.
Key Takeaways¶
Main Points:
– Expanded Tab Islands offer greater customization for organizing tabs by project or topic.
– Built-in AI is faster and more context-aware, aiding summarization, drafting, and task automation.
– The sidebar’s enhanced Google service integration and improved split-screen layouts boost multitasking capability.
Areas of Concern:
– Privacy and data handling with AI features and Google integrations need clear controls.
– Performance impact on lower-end devices with more features.
– Complexity risk: more options can overwhelm new users without effective onboarding.
Summary and Recommendations¶
Opera One R3 represents a meaningful expansion of the browser’s productivity toolkit. By extending Tab Islands, refining AI responsiveness, and broadening the sidebar’s capabilities, Opera aims to reduce context switching, accelerate information processing, and unify essential tools within a single interface. For users who regularly juggle multiple research streams, writing tasks, coding sessions, or cross-application workflows, R3 can offer tangible efficiency gains and a more streamlined workflow.
However, the value of these enhancements will depend on thoughtful adoption and careful configuration. Users should explore how to best structure Tab Islands to reflect their workstreams, tailor AI prompts and settings to avoid intrusive interactions, and adjust sidebar integrations to align with privacy preferences and tool ecosystems. It is advisable to enable features incrementally, monitor performance and battery impact, and review privacy settings to balance productivity with data protection.
For organizations and individual power users, R3 provides an opportunity to evaluate the browser as a central productivity platform. If the features prove to be stable, intuitive, and aligned with user needs, Opera could reinforce its position as a compelling alternative to traditional browsers by delivering a more integrated, task-oriented browsing experience.
Recommended actions:
– Update to Opera One R3 to access the extended Tab Islands, AI enhancements, and expanded sidebar features.
– Experiment with island organization schemes tailored to your projects, and customize visual cues for quick recognition.
– Test AI-assisted tasks on real workflows (summaries, drafting, data extraction) to gauge usefulness and adjust settings accordingly.
– Review privacy and data settings for AI and Google services, enabling controls that match your comfort level.
– Monitor performance across devices, particularly on laptops or tablets with limited memory, and disable features as needed to optimize responsiveness.
References¶
Original: https://www.techspot.com/downloads/393-opera-browser.html
Additional references:
- Opera official blog or release notes detailing Opera One R3 features and settings
- Independent reviews or user guides outlining Tab Islands and AI integration
- Privacy and security guidelines related to browser-integrated AI and third-party service integrations
*圖片來源:Unsplash*